
Reporting revenue and expenses in different periods can make it difficult to pair sales and expenses and assets and net income can be overstated. The direct write-off method doesn’t adhere to the expense matching principle—an expense must be recognized during the same period that the revenue is brought in. As a result, the direct write-off method violates the generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). To keep the business’s books accurate, the direct write-off method debits a bad debt account for the uncollectible amount and credits that same amount to accounts receivable. Reporting a bad debt expense will increase the total expenses and decrease net income.
Estimating the Bad Debt Expense
On the balance sheet, writing off inventory generally involves an expense debit for the value of unusable inventory and a credit to inventory. How do you record the sale of inventory to a customer direct write-off method who the credit manager deems will have a 10% chance of paying? The sale occurred December 1st 2015 and has payment due in 60days, so at year end December 31st 2015 the account is not yet due.
Netflix: a question of accounting methodology – Investors Chronicle
Netflix: a question of accounting methodology.
Posted: Thu, 07 Apr 2022 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Direct write-off method vs allowance method
Because it is an estimation, it means the exact account that is (or will become) uncollectible is not yet known. However, if the engineer goes bankrupt the next without paying for the software package, it becomes uncollected debt. That would overstate the bad debt expense for 2020 by $1,200 and understate for 2021 by the same amount.
- This is called the matching principle, according to Accounting Tools.
- Through the direct write-off method, we straightforwardly book a bad debt expense by debiting the bad debt expense account and crediting the accounts receivable account.
- The companies that qualify for this exemption, however, are typically small and not major participants in the credit market.
- After two months, the customer is only able to pay $8,000 of the open balance, so the seller must write off $2,000.
- The allowance for doubtful accounts is a contra asset account and is subtracted from Accounts Receivable to determine the Net Realizable Value of the Accounts Receivable account on the balance sheet.
- Because we identified the wrong account as uncollectible, we would also need to restore the balance in the allowance account.
- For example, a business records a sale on credit of $10,000, and records it with a debit to the accounts receivable account and a credit to the sales account.
Direct Write-Off vs. Allowance Method
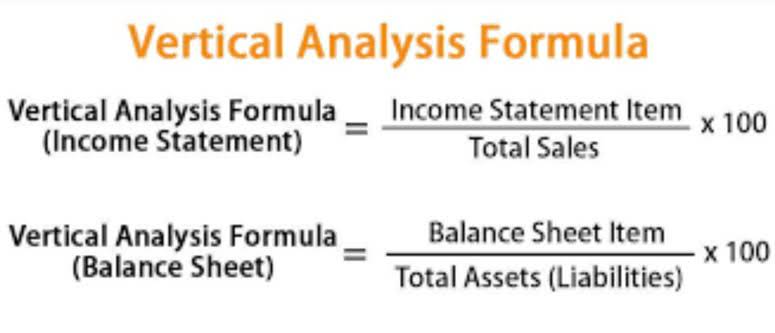
This estimate is the amount of expected uncollectible invoices and is reported as a bad debt expense for the year. You may notice that all three methods use the same accounts for the adjusting entry; only the method changes the financial outcome. Also note that it is a requirement that the estimation method be disclosed in the notes of financial statements so stakeholders can make informed decisions. The following table reflects how the relationship would be reflected in the current (short-term) section of the company’s Balance Sheet. As you’ve learned, the delayed recognition of bad debt violates GAAP, specifically the matching principle. Therefore, the direct write-off method is not used for publicly traded company reporting; the allowance method is used instead.
Income Statement Method for Calculating Bad Debt Expenses
As the accountant for a large publicly traded food company, you are considering whether or not you need to change your bad debt estimation method. You currently use the income statement method to estimate bad debt at 4.5% of credit sales. You are considering switching to the balance sheet aging of receivables method. This would split accounts receivable into three past- due categories and assign a percentage to each group. It is important to consider other issues in the treatment of bad debts.

- We know some accounts will go bad, but we do not have a name or face to attach to them.
- You currently use the income statement method to estimate bad debt at 4.5% of credit sales.
- The allowance method follows GAAP matching principle since we estimate uncollectible accounts at the end of the year.
- The direct write-off method doesn’t adhere to the expense matching principle—an expense must be recognized during the same period that the revenue is brought in.
- The general guidelines and principles, standards and detailed rules, plus industry practices that exist for financial reporting.
A provision is a probable outflow of cash for an uncertain amount of time. In the direct write-off method, bad debts are expensed out whenthey occur and are not related to the sales for the year. Let’s consider a situation where BWW had a $20,000 debit balance from the previous period. The direct write-off method lets you charge bad debts directly to an expense such as the Allowance for Bad Debt account used in the journal entries above.
Once you know how much from each time period, add them to get the total allowance balance. Allowance for Doubtful Accounts is where we store the nameless, faceless uncollectible amount. We know some accounts will go bad, but we do not have a name or face to attach to them.
If only one or the other were credited, the Accounts Receivable control account balance would not agree with the total of the balances in the accounts receivable subsidiary ledger. Without crediting the Accounts Receivable control account, the allowance https://www.bookstime.com/articles/dental-bookkeeping account lets the company show that some of its accounts receivable are probably uncollectible. The balance sheet method (also known as the percentage of accounts receivable method) estimates bad debt expenses based on the balance in accounts receivable.
- The allowance method adheres to the GAAP and reports estimates of bad debt expenses within the same period as sales.
- However, if the engineer goes bankrupt the next without paying for the software package, it becomes uncollected debt.
- In this example, the $85,200 total is the net realizable value, or the amount of accounts anticipated to be collected.
- Because it is an estimation, it means the exact account that is (or will become) uncollectible is not yet known.
- When the factor purchases the receivables without recourse, the company selling the receivables is not responsible for unpaid amounts.
- When doing the calculations, it is important to understand what the resulting number actually represents.
The accounts receivable aging method groups receivable accounts based on age and assigns a percentage based on the likelihood to collect. The percentages will be estimates based on a company’s previous history of collection. This distortion goes against GAAP principles as the balance sheet will report more revenue than was generated. This is why GAAP doesn’t allow the direct write off method for financial reporting.